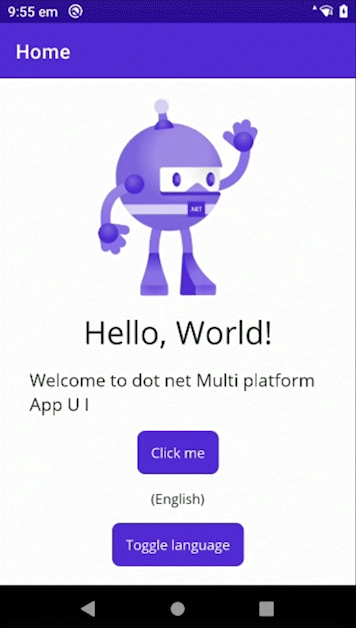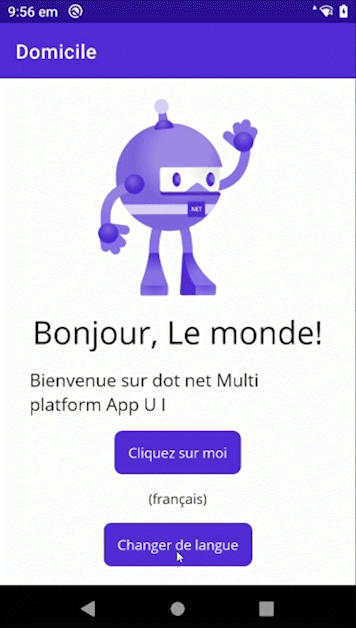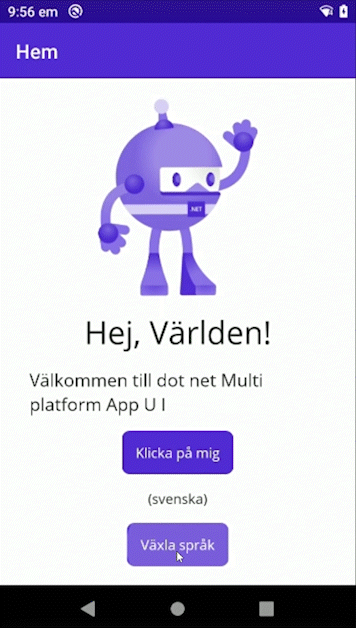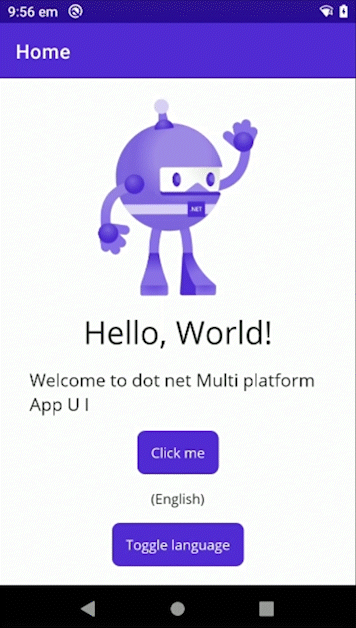
MAUI Lib - LocalizationResourceManager for MAUI!
I have been a fan of the Localization helpers and extensions in the Xamarin Community Toolkit and have been using this in my Xamarin projects. Since moving to .NET MAUI, I hoped for this to be part of the MAUI Community Toolkit. For good reasons the team has decided not to include this in MCT and a proposal is issued in the .NET Community Toolkit. But the XCT solution have dependencies to the Xamarin IMarkupExtension interface and the XCT WeakEventManager helper class, which makes it tricky to port to a non MAUI library. So until we have a official solution, or anyway is added to MCT, I decided to create a .NET MAUI library for this called LocalizationResourceManager.Maui!
Big shoutout to the original authors, Charlin Agramonte, Brandon Minnick, Maksym Koshovyi and the entire Xamarin Community Toolkit Team!
Library
The library is available both as a NuGet package and a MIT licensed repository at GitHub.
| Name | Nuget | GitHub |
|---|---|---|
| LocalizationResourceManager.Maui |  |
Compared to the original solution we have some enhanced and added features:
- Easy setup with builder pattern extension
- Supports multiple Resource managers
- Supports file based Resource managers
- Supports storing and restoring of the latest set culture
- New
ILocalizationResourceManagerinterface registered for constructor injection with DI - Stores current Default / System culture
- Supports Resource names with dots.
- Option to set a placeholder text to be displayed if text is not found.
TranslateBindingExtensionfor custom binding with format and plural support in XAML by Stephen Quan.- Uses the WeakEventManager (.NET MAUI)
For localized texts used in XAML and/or code behind, we still have:
TranslateExtension(XAML Markup Extension)LocalizedString(Track Culture Change in code behind)
Preparations
To use this library, there are some preperations you need to do in your .NET MAUI project/application:
- Set the
Assembly neutral languageto your default language.
(In project properties screen or directly in the project file!)
<NeutralLanguage>en</NeutralLanguage>
- Create/Add a
Resources File(resx) with the Resources Files Template for your default language. e.g. AppResources.resx - Create/Add a
Resources File(resx) for each additional language you want to support. e.g. AppResources-fr.rex for French
(Use same name as default file and add language code. List of all Language codes)
Easy setup
As many .NET MAUI libraries, I use the builder pattern for easy configuration. To setup the library, you use the UseLocalizationResourceManager extension method with the ILocalizationSettings settings methods for custom configuration.
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureFonts(fonts =>
{
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Regular.ttf", "OpenSansRegular");
fonts.AddFont("OpenSans-Semibold.ttf", "OpenSansSemibold");
})
.UseLocalizationResourceManager(settings =>
{
settings.AddResource(AppResources.ResourceManager);
settings.RestoreLatestCulture(true);
});
Settings contains 6 methods for configuration:
- AddResource
- AddFileResource
- InitialCulture
- RestoreLatestCulture
- SupportNameWithDots
- SuppressTextNotFoundException
AddResource
Used to add one or more Resource Managers. e.g. AppResources.ResourceManager, SpecialResources.ResourceManager etc.
Note: All resource libraries will be searched in the order they were added, until resource is found!
AddFileResource
Use to add file based Resource Managers. Enables the option to Create/Read/Write at runtime with ResourceWriter and ResourceReader.
InitialCulture
Set the initial/startup culture used for application. e.g. new CultureInfo(“fr”)
Default: Current System Culture
RestoreLatestCulture
Flag indicating if latest set culture should be restored on application startup.
Default: false
Note: This setting, if set to true, will override the InitalCulture setting!
SupportNameWithDots
Activate support for Resource Names with Dots when used with TranslateExtension. e.g. Text=”{localization:Translate Hello.World}”
Dots in names will be temporarily replaced by the substitution text to correctly be handled in the extension binding.
Option to set custom dot substitution. Default: “_”
SuppressTextNotFoundException
Ability to Suppress/Deactivate throwing the text not found exception with the option to set a placeholder text to be displayed if text is not found.
- UsePlaceholder flag to indicating if a placeholder text should be displayed if text is not found. (Optional, Default: false,
string.Empywill be returned) - Placeholder text to be displayed if text is not found, when UsePlaceHolder is activated. (Optional, Default: Resource name)
(“{0}” in the placeholder text, will be replaced with the resource name.)
Use in XAML
When used for localized texts in XAML pages, use the TranslateExtension:
- Add namespace reference to library.
- Use Translate extension with name of resource.
<ContentPage
x:Class="LocalizationResourceManager.Maui.Sample.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:localization="clr-namespace:LocalizationResourceManager.Maui;assembly=LocalizationResourceManager.Maui">
<Label
FontSize="18"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
SemanticProperties.Description="{localization:Translate WelcomeToMAUI}"
SemanticProperties.HeadingLevel="Level2"
Text="{localization:Translate WelcomeToMAUI}" />
Custom binding in XAML
Use the TranslateBindingExtension for custom binding with format and plural support.
Plural support in XAML
<Button
x:Name="CounterBtn"
Clicked="OnCounterClicked"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
SemanticProperties.Hint="{localization:Translate CounterBtnHint}"
Text="{localization:TranslateBinding Count, TranslateFormat=ClickedManyTimes, TranslateOne=ClickedOneTime, TranslateZero=ClickMe}" />
The way it works is:
TranslateFormat : (optional) similar to StringFormat, but the format comes from a string resource, e.g. “Clicked {0} times”
TranslateOne : (optional) similar to StringFormat, but used for when the binding value is one (1), e.g. “Clicked {0} time”
TranslateZero : (optional) similar to StringFormat, but used for when the binding value is zero (0), e.g. “Click Me”
Date/Time in XAML
public DateTime CurrentDateTime { get; set; } = DateTime.Now;
<!-- DateIs string resource: "Date is: {0}" -->
<Label Text="{localization:TranslateBinding CurrentDateTime, TranslateFormat=DateIs}/"/>
<! -- TimeIs string resource: "Time is: {0:HH}:{0:mm}:{0:ss}" -->
<Label Text="{localization:TranslateBinding CurrentDateTime, TranslateFormat=TimeIs}/" />
Currency in XAML
public decimal Price { get; set; } = 123.45;
<!-- TotalPrice string resource: "Total Price is: {0:C}" -->
<Label Text="{localization:TranslateBinding Price, TranslateFormat=TotalPrice}" />
Translate collections in XAML
TranslateValue : (optional) Apply localization changes to a view model, e.g.
public IList<string> Fruits { get; set; } = new List<string> { "LBL_APPLES", "LBL_ORANGES" };
<CollectionView ItemsSource="{Binding Fruits}">
<CollectionView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Label Text="{localization:TranslateBinding . , TranslateValue=True}"/>
<DataTemplate>
</CollectionView.ItemTemplate>
</CollectionView>
Translate true/false states in XAML
TranslateTrue : (optional) string resource used for when the binding value is true, e.g. “Yes”, “On”, “Activated”
TranslateFalse : (optional) string resource used for when the binding value is false, e.g. “No”, “Off”, “Deactivated”
public bool OrderSent { get; set; } = false;
<!-- Yes/No string resources: "Yes" / "No" -->
<Label Text="{localization:TranslateBinding OrderSent, TranslateTrue=Yes, TranslateFalse=No}" />
Use in Code
When used to handle localized texts in code behind or ViewModel, use the LocalizedString class:
- Add LocalizedString to code behind or ViewModel to track culture changes
- If needed, make binding to LocalizedString in XAML
public LocalizedString HelloWorld { get; } = new(() => $"{AppResources.Hello}, {AppResources.World}!");
…or to support multiple Resource managers…
public LocalizedString HelloWorld { get; }
public MainPage(ILocalizationResourceManager resourceManager)
{
HelloWorld = new(() => $"{resourceManager["Hello"]}, {resourceManager["World"]}!");
<Label
FontSize="32"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
SemanticProperties.HeadingLevel="Level1"
Text="{Binding HelloWorld.Localized}" />
Set and Get Culture
To handle and access the Current or Default Culture, we inject the ILocalizationResourceManager interface into our code behind or ViewModel to access the LocalizationResourceManager instance:
- Add the
ILocalizationResourceManagerinterface to your constructor and store locally for later access. - Use CurrentCulture property to Get or Set CurrentCulture. (All text accessed by
TranslateExtensionorLocalizedStringwill be updated immediately!) - Use DefaultCulture property to Get Default/System culture.
- Use GetValue method or Indexer operator [] to manually retrieve localized text based on Current culture.
- Use ReleaseAllResources method to Release/Close all resources for all registered resources. (Use before manually accessing registered file based resources!)
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
private readonly ILocalizationResourceManager resourceManager;
public MainPage(ILocalizationResourceManager resourceManager)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.resourceManager = resourceManager;
public string? CurrentCulture => resourceManager?.CurrentCulture.NativeName;
…or…
public LocalizedString CurrentCulture { get; }
public MainPage(ILocalizationResourceManager resourceManager)
{
CurrentCulture = new(() => resourceManager.CurrentCulture.NativeName);
One line to change Current Culture and Refresh ALL localized texts!
resourceManager.CurrentCulture = new CultureInfo("en");
Sample
Look at the Sample project for a example of how to use this library in an .NET MAUI application.